## Nanobots Developed to Treat Tooth Sensitivity **News Title:** IISc, startup develop magnetic nanobots to treat tooth sensitivity | Bengaluru News - Times of India **Report Provider:** The Times of India **Author:** TNN **Publication Date:** August 13, 2025 ### Overview Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), in collaboration with Bengaluru-based deep-tech startup Theranautilus, have engineered "CalBots," magnetic nanobots designed to treat tooth sensitivity. These nanobots aim to seal the source of pain within the tooth's dentinal tubules. ### Key Findings and Technology * **CalBots:** These are magnetic nanobots, measuring **400 nanometres** in size, loaded with a calcium silicate-based bioceramic formula. * **Mechanism of Action:** CalBots are designed to travel up to **500 micrometres** deep into the dentinal tubules, which are tiny tunnels in the tooth leading to nerve endings. * **Guided Assembly:** Guided by an external magnetic field, the nanobots self-assemble into stable, cement-like plugs. * **Function:** These plugs recreate the tooth's natural barrier, offering a potential solution for lasting relief from tooth sensitivity. * **Bioceramic Formulation:** The nanobots utilize a novel class of bioceramic cement specifically formulated for hypersensitivity, aiming for deeper penetration and longer-lasting effects compared to existing bioceramics used in orthopaedics and dentistry. ### Impact and Efficacy * **Prevalence of Tooth Sensitivity:** Dental hypersensitivity affects nearly **one in four people worldwide**. It occurs when enamel erosion or gum recession exposes the dentine layer, making the tubules within it direct pathways to nerves. * **Testing Results:** * **Extracted Human Teeth:** CalBots were applied to extracted human teeth under a magnetic field for **20 minutes**. High-resolution imaging confirmed that the bots successfully sealed the dentinal tubules by forming deep, stable plugs. * **Animal Trials (Mice):** * Sensitive mice, which avoided cold water, resumed drinking it after treatment. * The researchers observed **100% behavioural recovery** in these mice, indicating a significant positive outcome. * **Safety:** CalBots are made from materials classified as 'generally recognised as safe' (GRAS) and have passed toxicity tests in mice. ### Significance and Future Outlook * **Novel Approach:** The development represents a novel approach to treating tooth sensitivity, addressing the problem at its source. * **Potential Healthcare Impact:** The technology is seen as a compelling demonstration of what nanorobotics can achieve and its potential to significantly impact future healthcare. * **"Tiny Mechanical Surgeons":** The researchers view this innovation as a step towards the concept of "tiny mechanical surgeons" envisioned by Richard Feynman, highlighting the regenerative and active nature of the nanomaterial. ### Key Personnel * **Shanmukh Peddi:** Postdoctoral researcher at IISc's Centre for Nano Science and Engineering (CeNSE) and co-founder of Theranautilus. * **Ambarish Ghosh:** Professor at CeNSE and one of the study's corresponding authors. * **Debayan Dasgupta:** Former PhD student at CeNSE and co-founder of Theranautilus.
IISc, startup develop magnetic nanobots to treat tooth sensitivity | Bengaluru News - Times of India
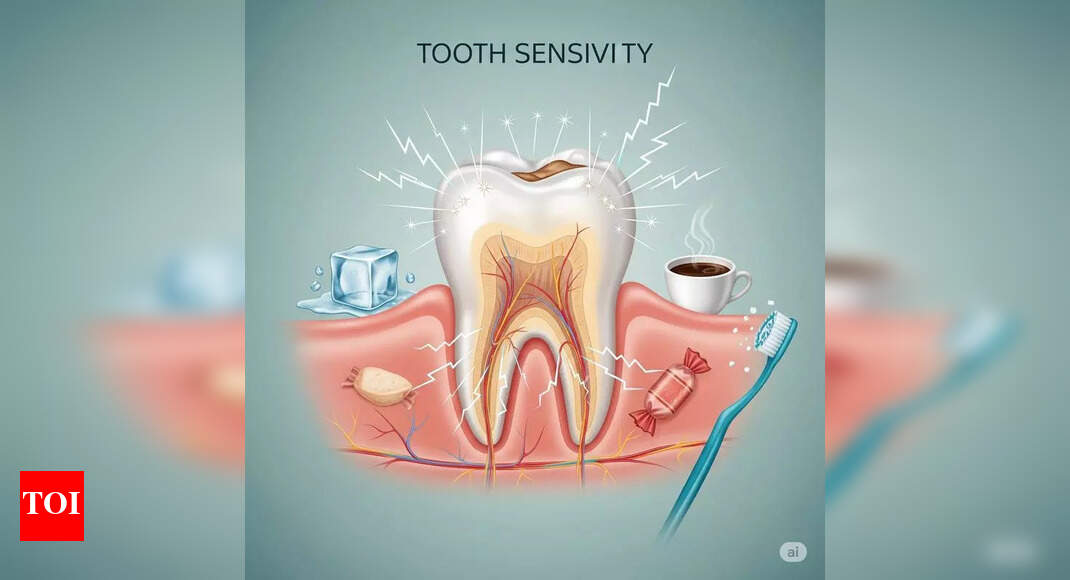
Read original at The Times of India →Bengaluru: For millions of people, the sudden, sharp pain of tooth due to sensitivity can turn a sip of cold water into a jolt. Now, researchers at Indian Institute of Science (IISc), in collaboration with Bengaluru-based deep-tech startup Theranautilus, have engineered "CalBots" – magnetic nanobots that can seal the problem at its source.
As per IISc, CalBots are 400-nanometre particles loaded with a calcium silicate-based bioceramic formula, designed to travel 500 micrometres deep inside dentinal tubules, the tiny tunnels in the tooth that lead to nerve endings. Guided by an external magnetic field, the bots can then self-assemble into stable, cement-like plugs that recreate the tooth's natural barrier.
One application, the team said, can offer lasting relief.Dental hypersensitivity affects nearly one in four people worldwide and occurs when enamel erosion or gum recession exposes the dentine layer beneath, IISc said. The tubules in dentine act as direct pathways to the nerves, which is why even mild temperature changes can trigger pain.
"We wanted a technology that solves a real problem in a way that no one's attempted before," said Shanmukh Peddi, postdoctoral researcher at IISc's Centre for Nano Science and Engineering (CeNSE) and co-founder of Theranautilus.The team used a completely new class of bioceramic cement for the nanobots.
While bioceramics are common in orthopaedics and dentistry, the formulation was designed specifically for hypersensitivity – to travel deeper and last longer.To test the approach, they worked first on extracted human teeth. "On these samples, we applied CalBots under a magnetic field for 20 minutes, during which the bots sealed the dentinal tubules by forming deep, stable plugs, a result confirmed through high-resolution imaging," Peddi said.
They then moved to animal trials. "Healthy mice drank both cold and room temperature water equally. But sensitive mice completely avoided cold water. After treatment, they started drinking it again. We saw 100% behavioural recovery. That was a big moment for us," he said.The CalBots are made entirely from materials classified as ‘generally recognised as safe' and passed toxicity tests in mice.
"This is a compelling demonstration of what nanorobotics can achieve, and how they could significantly impact future healthcare," said Ambarish Ghosh, professor at CeNSE and one of the study's corresponding authors.Debayan Dasgupta, former PhD student at CeNSE and co-founder of Theranautilus, sees this as part of a bigger technological shift.
"We've created a regenerative, active nanomaterial, a step towards the kind of ‘tiny mechanical surgeons' Richard Feynman once envisioned," he said.